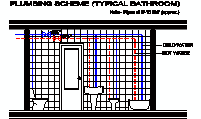
CAD Blocks categories
 3D models
3D models home furniture
home furniture sanitary ware - bathrooms
sanitary ware - bathrooms professional equipment
professional equipment doors and windows
doors and windows people and animals
people and animals plants and trees
plants and trees vehicles - transports
vehicles - transports architectural details
architectural details mechanical - electrical
mechanical - electrical urban planning - civil works
urban planning - civil works safety health construction
safety health construction accessible design
accessible design drawing sheet
drawing sheet signals
signals construction machinery
construction machinery accessories and objects
accessories and objects maps and street maps
maps and street maps
![]() Architectural Graphic Standards - Construction Details
includes CAD drawings for essential architectural and construction elements. Featured items include vertical sections, stair designs, escalators, moving walkways, and roofing solutions such as curved tiles and corrugated sheets.
Architectural Graphic Standards - Construction Details
includes CAD drawings for essential architectural and construction elements. Featured items include vertical sections, stair designs, escalators, moving walkways, and roofing solutions such as curved tiles and corrugated sheets.
Other highlights include railing systems, steel beams, precast concrete components, ventilation systems, decorative lattices, nuts, and wall plugs, providing practical resources for architectural projects.
Railings
Railings are essential building components that provide safety and support in various structures. Commonly made from materials like metal, wood, or PVC, railings enhance aesthetics while ensuring compliance with safety regulations. Their installation requires careful consideration of height and spacing to prevent falls, typically around 1.1 meters (43.3 inches) high. While they offer durability, weather resistance is a key factor for outdoor railings. Alternatives include glass or cable systems, providing different visual impacts.
PVC - Aluminum Windows and Doors
When choosing between PVC and aluminum windows and doors, both materials offer distinct advantages. PVC is known for its excellent insulation and low maintenance, while aluminum provides strength and a modern aesthetic. Installation involves precise measurements and careful sealing to prevent air leaks. PVC windows typically measure 1.2 meters (47.2 inches) in height, while aluminum can be adjusted for custom designs. Consideration of environmental impact and energy efficiency is essential when selecting materials.
Stairs
Stairs provide vertical access in buildings and come in various designs, including straight, spiral, and curved. Construction typically involves wood, concrete, or metal, with a standard rise of 0.175 meters (6.9 inches) per step. Proper installation is vital for safety, adhering to local building codes. Advantages include space efficiency and aesthetics, while disadvantages may involve steepness impacting accessibility. Alternatives like ramps are recommended for improved accessibility for individuals with mobility challenges.
Reinforced Concrete Structures
Reinforced concrete structures combine concrete and steel to enhance tensile strength, making them ideal for high-rise buildings and bridges. Construction involves pouring concrete around steel bars, ensuring durability. Typical dimensions for beams may reach 0.3 meters (11.8 inches) wide. Advantages include fire resistance and longevity, while disadvantages can include weight and potential cracking. Alternatives like pre-stressed concrete offer improved performance under tension.
Building Components
Building components refer to individual parts of a structure, such as walls, roofs, and foundations. Each component must be designed for functionality and aesthetic appeal. Common materials include concrete, wood, and metal. Proper installation techniques ensure structural integrity. While components contribute to the overall strength of a building, they also require careful planning to accommodate loads and stresses. Modular components present an efficient alternative, facilitating quicker assembly on-site.