CAD Blocks categories
 3D models
3D models home furniture
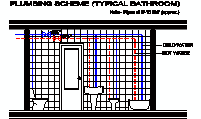
home furniture sanitary ware - bathrooms
sanitary ware - bathrooms professional equipment
professional equipment doors and windows
doors and windows people and animals
people and animals plants and trees
plants and trees vehicles - transports
vehicles - transports architectural details
architectural details mechanical - electrical
mechanical - electrical urban planning - civil works
urban planning - civil works safety health construction
safety health construction accessible design
accessible design drawing sheet
drawing sheet signals
signals construction machinery
construction machinery accessories and objects
accessories and objects maps and street maps
maps and street maps
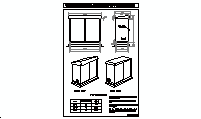
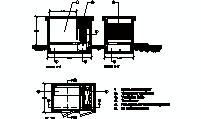
Reinforced Concrete Beam Rebar Design

size: 11 kb
category: architectural details
related categories:
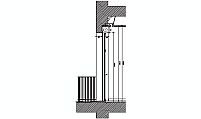
description: A technical drawing of a reinforced concrete beam rebar arrangement, showing precise dimensions, spacings, and detailed specifications for construction.
file extension: .dwg CAD - AutoCAD software
Structural Rebar Details for Concrete Beams
Beam Rebar Configuration
The reinforced concrete beam in the diagram illustrates a detailed arrangement of longitudinal and transverse reinforcement. Longitudinal bars are carefully positioned to counteract tensile stresses, while stirrups provide resistance against shear forces. This configuration enhances the structural integrity of the beam under heavy loads and dynamic forces.
Other rebar configurations, such as those used in cantilever beams or continuous beams, often adapt similar principles with variations in the number of bars or spacing. These configurations are optimized to handle specific load conditions, making them versatile for diverse structural applications.
Dimensions and Spacing
The rebar in the diagram includes diameters of 16 mm, 12 mm, and 6 mm. Beam widths are specified at 30x30 cm and 30x50 cm, while column sections measure 30x30 cm. The stirrups have a diameter of 6 mm and are spaced 16 cm or 18 cm apart, depending on the type of stress the beam is subjected to. This precise arrangement ensures structural efficiency and stability.
Stirrups play a crucial role in reinforced concrete beams by resisting shear forces and holding the longitudinal bars in position. They prevent the concrete from cracking under diagonal tension and ensure the beam's durability by distributing loads evenly. By maintaining the integrity of the rebar cage, stirrups contribute to the overall stability and load-bearing capacity of the beam, making them indispensable in structural design.
Construction Techniques
Reinforced concrete beams are built using a systematic process starting with formwork preparation. Rebar cages are assembled and secured, ensuring accurate positioning for tensile and shear resistance. Concrete is poured carefully, and vibrators are used to eliminate air pockets and achieve a dense, compact mix.
To ensure durability, the curing process plays a critical role. Proper curing helps the concrete reach its designed strength and ensures that the bond between the steel and concrete remains strong, protecting the beam against environmental factors and long-term wear.
Advantages of Rebar
Reinforced concrete beams excel in providing superior tensile and compressive strength, making them a cornerstone of modern construction. Rebar prevents cracks from propagating, ensuring that the beam can handle high loads while maintaining structural integrity over time.
Compared to alternative materials like timber or steel beams, reinforced concrete is more cost-effective and versatile. It can be used in a variety of applications, from residential buildings to large-scale infrastructure, adapting to diverse architectural and engineering needs.
Origins and Evolution
The invention of reinforced concrete in the 19th century revolutionized construction by combining concrete's compressive strength with steel's tensile strength. This innovation allowed for the creation of stronger, more versatile structures that could withstand complex load conditions.
Over time, advancements in material science and engineering have improved the efficiency of reinforced concrete. Modern techniques, such as pre-stressing and post-tensioning, have further enhanced its load-bearing capabilities, ensuring that reinforced concrete remains a vital element in global construction practices.