CAD Blocks categories
 3D models
3D models home furniture
home furniture sanitary ware - bathrooms
sanitary ware - bathrooms professional equipment
professional equipment doors and windows
doors and windows people and animals
people and animals plants and trees
plants and trees vehicles - transports
vehicles - transports architectural details
architectural details mechanical - electrical
mechanical - electrical urban planning - civil works
urban planning - civil works safety health construction
safety health construction accessible design
accessible design drawing sheet
drawing sheet signals
signals construction machinery
construction machinery accessories and objects
accessories and objects maps and street maps
maps and street maps
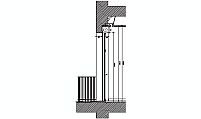
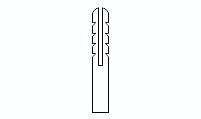
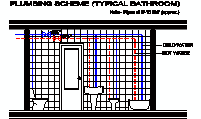
Ventilation Duct Terminal - Free CAD Block

size: 5 kb
category: architectural details
related categories:
description: front elevation of a ventilation duct terminal, designed to facilitate airflow in interior rooms lacking direct external windows.
file extension: .dwg CAD - AutoCAD software
Detailed Guide of Ventilation Duct Terminal for Interior Rooms
Overview of Ventilation Duct Terminals
Ventilation duct terminals are crucial components in HVAC systems, designed to facilitate the exchange of indoor and outdoor air. These prefabricated elements, typically made from concrete or plastic, are installed at the end of ventilation ducts to ensure proper airflow in interior rooms without direct access to external windows. Their design allows for the upward movement of air, utilizing roof currents to enhance ventilation efficiency.
In addition to promoting airflow, the shape of these terminals is engineered to prevent the ingress of water into the duct system. This dual functionality ensures that interior spaces such as bathrooms, storage rooms, and other secondary rooms maintain adequate air quality without the risk of moisture-related issues. The integration of ventilation duct terminals into building designs reflects a commitment to occupant health and structural integrity.
Regulatory Standards for Interior Room Ventilation
In many developed countries, building codes permit the use of ventilation duct terminals for interior rooms without direct external windows, provided certain conditions are met. In the United States, standards such as the International Mechanical Code (IMC) and ASHRAE guidelines specify the minimum ventilation rates for these rooms. Bathrooms, storage rooms, and similar secondary spaces are typically allowed to use duct terminals when direct ventilation is not feasible.
European countries, including the UK, also allow interior spaces to use ventilation terminals under regulations such as Part F of the UK Building Regulations. These codes require systems to maintain adequate airflow and air exchange to prevent the buildup of moisture and odors. The systems must ensure fresh air intake and proper expulsion of stale air, complying with minimum rates set by local or national standards.
Functionality and Design of Ventilation Duct Terminals
Ventilation duct terminals are designed to ensure effective airflow while preventing water ingress. According to common building standards, the minimum cross-sectional area of the ducts should be 4 inches by 4 inches (100 mm by 100 mm) for small rooms such as bathrooms, with larger rooms requiring proportional increases in duct dimensions. The terminal openings should provide a free area of at least 60 square inches (0.04 square meters) to facilitate sufficient ventilation.
The final element, or terminal, should extend a minimum of 12 inches (300 mm) above the highest point of the roof, such as the ridge, to ensure uninterrupted airflow. It must be placed at least 3 feet (1 meter) away from any obstructions like chimneys or walls that could impede air movement. Materials used for these terminals are typically weather-resistant, including concrete, plastic, or galvanized steel, to withstand environmental conditions and provide durability. The design includes sloped surfaces and protective grilles to prevent rainwater ingress while allowing air to flow freely.
Advantages of Ventilation Duct Terminals
Ventilation duct terminals offer numerous advantages, including improved air quality and enhanced moisture control. By providing a reliable outlet for stale air, these systems help maintain a healthy indoor environment, particularly in spaces without direct external windows. Their design ensures effective airflow while preventing water infiltration, reducing the risk of mold or structural damage.
Compared to traditional methods of ventilation, such as direct exhaust fans, duct terminals are more versatile and can be integrated into a wider variety of building designs. They are especially beneficial in multi-story buildings or structures where space constraints make other solutions impractical. Their durable construction and minimal maintenance requirements make them a cost-effective choice for long-term use.
Evolution and Applications of Ventilation Duct Terminals
The concept of ventilation duct terminals dates back to early architectural designs where air circulation was achieved through natural methods such as vents and louvers. Over time, advancements in building technology have led to the development of modern duct terminals, which incorporate features such as weather-resistant materials and optimized airflow designs. These improvements have made them indispensable in contemporary construction.
Today, ventilation duct terminals are widely used in both residential and commercial buildings. Their applications range from ensuring adequate airflow in secondary rooms, such as bathrooms and storage spaces, to providing efficient ventilation in industrial facilities. As building codes continue to evolve, these terminals remain a key solution for meeting ventilation requirements while maintaining architectural aesthetics.