CAD Blocks categories
 3D models
3D models home furniture
home furniture sanitary ware - bathrooms
sanitary ware - bathrooms professional equipment
professional equipment doors and windows
doors and windows people and animals
people and animals plants and trees
plants and trees vehicles - transports
vehicles - transports architectural details
architectural details mechanical - electrical
mechanical - electrical urban planning - civil works
urban planning - civil works safety health construction
safety health construction accessible design
accessible design drawing sheet
drawing sheet signals
signals construction machinery
construction machinery accessories and objects
accessories and objects maps and street maps
maps and street maps
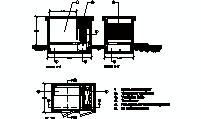
Elevator Cabin Section View with Hydraulic System

size: 5 kb
category: electrical, mechanical and HVAC
related categories:
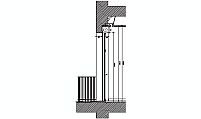
description: A detailed horizontal section of an elevator cabin with hydraulic operation, featuring telescopic doors and guide profiles. The interior shaft dimensions are 160 cm x 145 cm (approximately 63 in x 57 in), with a entry width of 80 cm (approximately 31.5 in).
file extension: .dwg CAD - AutoCAD software
Detailed Elevator Design: Dimensions, Accessibility, and More
Technical Description of Elevator Cabin
This horizontal section of the elevator cabin depicts a hydraulic lift without a counterweight. The internal dimensions measure 160 cm x 145 cm (approximately 63 in x 57 in), while the clear entry width is 80 cm (around 31.5 in). The telescopic doors retract to the right, providing efficient space utilization. The right side houses the guide system and profiles essential for the elevator's secure operation.
Other common designs in the same category include elevators with counterweights or traction systems. However, hydraulic lifts like this offer advantages such as compactness and the ability to fit in narrower shafts, making them suitable for residential or low-rise buildings.
Common Dimensions and Load Capacity
In construction systems, the shaft dimensions typically align with standard elevator cabins of this size. The cabin's interior dimensions of 63 in x 57 in comfortably allow space for 4 to 5 occupants, supporting a maximum load of 800 lbs (around 363 kg). The door width of 31.5 in provides sufficient clearance for accessibility.
Based on the drawing, the shaft's dimensions are confirmed to align with these standards, ensuring compatibility with modern hydraulic elevator systems. Accurate conversions from metric units validate these specifications for typical architectural uses.
Construction Methods and Compatibility
- What materials are used for the elevator frame?
- Steel and aluminum profiles are commonly used for structural stability and corrosion resistance.
- How are hydraulic systems installed?
- The hydraulic pump and cylinder are typically placed at the base of the shaft, reducing the need for overhead machinery.
- What type of doors are compatible?
- Telescopic doors, like those shown, are ideal for compact spaces and ensure smooth operation.
- Can this cabin fit in older buildings?
- Yes, hydraulic systems are especially suitable for retrofitting due to their flexibility and minimal spatial requirements.
- What additional safety features are recommended?
- Safety measures include emergency braking systems, door sensors, and fire-resistant materials.
Advantages of Hydraulic Elevator Systems
Hydraulic elevators like this one offer several advantages over traditional counterweight systems. They require less overhead space, making them ideal for buildings with height restrictions. Their compact design also reduces installation complexity and costs.
Additionally, these elevators can handle heavier loads relative to their size, are quieter in operation, and allow more design flexibility. These features make them a popular choice for residential and low-rise buildings.
Evolution and Global Alternatives
The hydraulic elevator's origins date back to the mid-20th century, evolving as an alternative to traditional traction systems. Over time, innovations like telescopic doors and compact hydraulic mechanisms have enhanced their efficiency and applicability in modern construction.
Globally, similar systems like screw-drive elevators in Europe and pneumatic elevators in South America offer alternatives tailored to regional needs. These systems share the goal of maximizing space and minimizing structural demands.