CAD Blocks categories
 3D models
3D models home furniture
home furniture sanitary ware - bathrooms
sanitary ware - bathrooms professional equipment
professional equipment doors and windows
doors and windows people and animals
people and animals plants and trees
plants and trees vehicles - transports
vehicles - transports architectural details
architectural details mechanical - electrical
mechanical - electrical urban planning - civil works
urban planning - civil works safety health construction
safety health construction accessible design
accessible design drawing sheet
drawing sheet signals
signals construction machinery
construction machinery accessories and objects
accessories and objects maps and street maps
maps and street maps
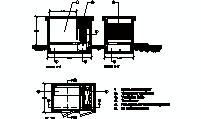
Precast Concrete Beam - Free CAD Block
size: 5 kb
category: architectural details
related categories:
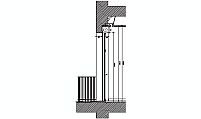
description: front elevation of a precast concrete beam designed for unidirectional slab systems, for integration with hollow blocks.
file extension: .dwg CAD - AutoCAD software
Detailed Information of Precast Concrete Beam for Unidirectional Slabst
Overview of Precast Concrete Beams in Unidirectional Slab Systems
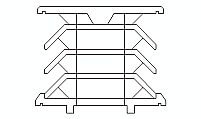
Precast concrete beams are integral components in unidirectional slab systems, commonly known as beam and hollow block constructions. These beams are placed longitudinally and rest on concrete girders, with anchorage provided by steel reinforcing bars at the upper part of the beam. Over these beams, hollow blocks—either prefabricated concrete or ceramic—are positioned to act as permanent formwork.
Once the beams, hollow blocks, and steel reinforcements are in place, an electrowelded mesh is added, and concrete is poured to fill the gaps, excluding the areas occupied by the hollow blocks. This creates a unified slab system with enhanced strength and load distribution. Precast concrete beams are widely used due to their efficiency, structural integrity, and ease of installation.
Regulatory Standards for Precast Concrete Beams
Precast concrete beams must comply with rigorous standards to ensure structural safety and performance. In the United States, the ACI 318 code outlines the requirements for the design and construction of concrete structures, including precast elements. In Europe, the relevant standard is EN 13225, which specifies the requirements for precast concrete structural components, including quality control, tolerances, and material specifications.
These standards ensure that precast beams meet criteria such as load-bearing capacity, durability, and fire resistance. Additionally, regional standards may apply to specific applications, such as seismic zones or extreme climates. Compliance with these regulations is critical for ensuring the safety and longevity of buildings incorporating precast concrete beams.
Dimensions and Components of Precast Concrete Beams
Precast concrete beams typically measure between 10 cm to 15 cm (4 in to 6 in) in width and 15 cm to 25 cm (6 in to 10 in) in height. The length varies based on the span of the structure, with common lengths ranging from 2 meters to 6 meters (6.6 ft to 19.7 ft). The interaxis distance, or the spacing between beams, is generally determined by the width of the hollow blocks, which ranges from 40 cm to 60 cm (16 in to 24 in).
The beams include a lattice of steel reinforcements consisting of upper and lower longitudinal bars connected by diagonal braces. This reinforcement ensures the beam's structural integrity during installation and under load. The steel reinforcements are made of corrugated bars to improve adhesion with the concrete. Hollow blocks are placed between the beams to act as permanent formwork, reducing the overall weight of the slab while maintaining strength.
Advantages of Precast Concrete Beams
Using precast concrete beams in unidirectional slabs offers numerous advantages. These include faster construction times, as the beams and hollow blocks are prefabricated and ready for installation upon delivery. The system reduces the need for temporary formwork, minimizing material waste and labor costs. Additionally, the integration of hollow blocks reduces the overall weight of the slab without compromising its structural integrity.
Precast beams also ensure high-quality control, as they are manufactured in a controlled environment. This leads to consistent dimensions, better durability, and improved performance under load. Their modular nature allows for flexibility in design, making them suitable for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. The combination of durability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness makes precast concrete beams a preferred choice for modern construction projects.
History and Applications of Precast Concrete Beams
The use of precast concrete beams dates back to the early 20th century when the demand for efficient and reliable construction methods increased. Their development revolutionized building practices, offering a faster and more economical alternative to traditional cast-in-place concrete. Over time, advancements in materials and manufacturing processes have enhanced their performance and expanded their applications.
Today, precast concrete beams are used in a variety of structures, including residential buildings, commercial developments, parking garages, and bridges. Their versatility, combined with their structural efficiency, makes them an ideal choice for projects requiring durability, speed, and adaptability. As the construction industry continues to prioritize sustainability and cost-effectiveness, precast concrete beams remain a cornerstone of modern engineering.