CAD Blocks categories
 3D models
3D models home furniture
home furniture sanitary ware - bathrooms
sanitary ware - bathrooms professional equipment
professional equipment doors and windows
doors and windows people and animals
people and animals plants and trees
plants and trees vehicles - transports
vehicles - transports architectural details
architectural details mechanical - electrical
mechanical - electrical urban planning - civil works
urban planning - civil works safety health construction
safety health construction accessible design
accessible design drawing sheet
drawing sheet signals
signals construction machinery
construction machinery accessories and objects
accessories and objects maps and street maps
maps and street maps
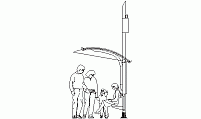
Plan View of a Reinforced Bus Shelter Structure

size: 31 kb
category: street furniture
related categories:
description: CAD drawing of a bus shelter in plan view, featuring a reinforced canopy measuring 171 inches (4.34 meters) in length and 59 inches (1.5 meters) in width.
file extension: .dwg CAD - AutoCAD software
Detailed CAD Block of a Bus Shelter in Plan View
Features of the Bus Shelter in Plan View
The CAD drawing represents a modern bus shelter as seen from above, with its main visible feature being the roof. The shelter itself is designed to provide coverage for passengers waiting for public transportation. From this plan view, the rectangular layout of the roof is evident, with dimensions of 171 inches (4.34 meters) in length and 59 inches (1.5 meters) in width.
This roof is part of a larger shelter structure, which includes supporting poles and seating areas (not visible in this view). The roof’s layout suggests that the shelter is optimized for urban environments, combining functionality with a compact footprint suitable for high-traffic areas.
Dimensions of the Shelter and Market Comparisons
This specific shelter features a roof measuring 171 inches (4.34 meters) in length and 59 inches (1.5 meters) in width. These dimensions are well-suited for accommodating several passengers while maintaining a compact size that can fit into dense urban areas. The design reflects an efficient use of space without sacrificing coverage or stability.
In comparison, standard bus shelters in the United States and Canada typically range from 144 to 192 inches (3.66 to 4.88 meters) in length and 48 to 72 inches (1.22 to 1.83 meters) in width. In Europe and the UK, shelters can measure between 120 and 200 inches (3.05 to 5.08 meters) in length, while in Asia and Japan, more compact designs are common, ranging from 96 to 144 inches (2.44 to 3.66 meters). These variations reflect regional priorities, such as passenger volume, climate conditions, and available space.
Construction and Visible Details from the Plan View
Although the drawing primarily highlights the roof, the visible details suggest key construction elements of the shelter. The roof’s structure is a hip roof, featuring sloping sides that meet at a ridge (horizontal top line) and hip rafters (diagonal edges). These intersections improve water drainage and wind resistance, contributing to the shelter’s overall durability.
Two small ornamental elements, likely roof pinnacles, are visible at the ends of the ridge. These details enhance the visual appeal of the structure. The roof appears to be constructed with corrugated metal panels featuring longitudinal reinforcements, which increase stability and reduce deformation under environmental loads. These elements are essential for withstanding varied weather conditions while maintaining a lightweight, low-maintenance design.
Functional Benefits of the Shelter
The shelter’s design, as seen from above, offers a range of functional benefits. Its roof dimensions of 171 inches (4.34 meters) by 59 inches (1.5 meters) provide sufficient coverage for passengers, protecting them from rain, sun, and wind. The sloping roof ensures efficient water runoff, while the longitudinal reinforcements improve stability and longevity.
Additionally, the compact footprint of the shelter allows it to be placed in a variety of urban settings, from high-traffic transit hubs to smaller suburban stops. The inclusion of decorative elements, such as the pinnacles, adds to its visual appeal, making it an attractive feature in public spaces while fulfilling its primary purpose of providing protection and comfort.
Evolution of Bus Shelters and Their Roof Designs
Bus shelters have evolved significantly over time, transitioning from basic structures with minimal protection to modern, highly engineered designs. The roof design in this shelter, characterized by its hip roof structure, reflects advancements in urban infrastructure that prioritize both functionality and aesthetics.
Globally, shelters are adapted to regional needs. In colder climates like Canada and Scandinavia, roofs are designed with steep slopes to prevent snow accumulation, while tropical regions prioritize ventilation and extended overhangs for shade. This particular design, with its compact dimensions and reinforced metal panels, represents a versatile solution that can be customized for various environments and user demands.